JENKINS_HOME
+- builds (build records)
+- [BUILD_ID] (subdirectory for each build)
+- build.xml (build result summary)
+- changelog.xml (change log)
+- config.xml (Jenkins root configuration file)
+- *.xml (other site-wide configuration files)
+- fingerprints (stores fingerprint records, if any)
+- identity.key.enc (RSA key pair that identifies an instance)
+- jobs (root directory for all Jenkins jobs)
+- [JOBNAME] (sub directory for each job)
+- config.xml (job configuration file)
+- [FOLDERNAME] (sub directory for each folder)
+- config.xml (folder configuration file)
+- jobs (subdirectory for all nested jobs)
+- plugins (root directory for all Jenkins plugins)
+- [PLUGIN] (sub directory for each plugin)
+- [PLUGIN].jpi (.jpi or .hpi file for the plugin)
+- secret.key (deprecated key used for some plugins' secure operations)
+- secret.key.not-so-secret (used for validating _$JENKINS_HOME_ creation date)
+- secrets (root directory for the secret+key for credential decryption)
+- hudson.util.Secret (used for encrypting some Jenkins data)
+- master.key (used for encrypting the hudson.util.Secret key)
+- InstanceIdentity.KEY (used to identity this instance)
+- userContent (files served under your https://server/userContent/)
+- workspace (working directory for the version control system)
Configuring the System
Jenkins stores its global configuration in files on the Jenkins controller. Administrators and privileged users modify the global configuration from the Jenkins configuration pages.
Jenkins home directory
The JENKINS_HOME directory is the root of the directory structure on disk that Jenkins uses to perform builds and keep archives.
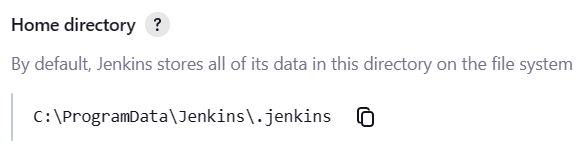
The Jenkins home directory is listed in Manage Jenkins > System under the Home directory heading.
-
On Windows by default, this is set to
C:\ProgramData\Jenkins\.jenkins. -
On Ubuntu by default, this is set to
~/.jenkins.
But you can change this in one of the following ways:
-
Set the
JENKINS_HOMEenvironment variable. -
Set the
JENKINS_HOMEJava system property.
You can change this location after you’ve used Jenkins for a while, too. To do this:
-
Stop Jenkins completely.
-
Move the contents from the old
JENKINS_HOMEto the new location. -
Set the
JENKINS_HOMEvariable to the new location. -
Restart Jenkins.
The directory structure of the JENKINS_HOME tree is often structured as follows:
Please submit your feedback about this page through this quick form.
Alternatively, if you don't wish to complete the quick form, you can simply indicate if you found this page helpful?
See existing feedback here.